What is Pulpectomy?
When the nerve of a baby’s tooth becomes infected, a Pulpectomy can save the tooth. A pulpectomy is a dental procedure in which all the pulp in the pulp chamber and root canal of a tooth is removed. This procedure is recommended when the pulp has become infected and the infection cannot be resolved. The goal of the procedure is to prevent the infected pulp from spreading the infection that could lead to the loss of one or more teeth.
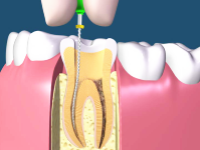
What is Pulpotomy?
A Pulpotomy is when the inflamed pulp chamber, usually on a baby molar, is removed, the area is sterilized, and the chamber is sealed. When a cavity gets really deep, close to the pulp of a tooth or even into the pulp, the pulpal tissue becomes irritated and inflamed. If the inflammation and infection continues without treatment, the tooth will eventually form abscess. In baby molars, a Pulpotomy is used in the process of trying to save and restore the tooth. First, the decay is removed, and then the pulp chamber (the top part, not the root canals) is removed usually with a high-speed bur or spoon excavator. A small cotton ball damp with form cresol is placed to “mummify” the pulp stumps and to sterilize the area. After a couple of minutes, the cotton ball is removed and the opening is sealed usually with a Zinc Oxide and Eugenol material like IRM. After a pulpotomy on a baby molar, it is usually necessary to place a stainless steel crown to restore the tooth. Pulpotomies have reasonably good prognosis, but cannot save an already abscessed tooth.

Stainless steel crowns for children
Stainless steel crowns are made specifically for primary teeth. With stainless steel crowns even severely damaged teeth can be retained for chewing and space maintenance. Small cavities in primary teeth can be repaired with fillings, because after we remove the decayed part of the tooth, there’s still plenty of remaining natural tooth structure. However, when a primary tooth has a large cavity, there may not be enough tooth structure left to place a filling. For this reason, we use crowns to repair large cavities in primary teeth. A crown covers the damaged tooth to strengthen and protect it.
Crowns for primary teeth are most often pre-made of stainless steel, and can be adapted to your child’s tooth and cemented in place in only one appointment.
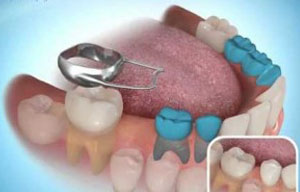
Situations suitable for stainless steel crowns
- Deep cavities or large carious lesions.
- Endodontically treated teeth.
- Primary molars with enamel defects.
- Severely damaged permanent teeth in young patients as a provisional crown until the laboratory constructed “permanent crowns” can be fitted.
Crowns for the front teeth
There are also a number of types of crowns for the front teeth. The reason for caries in toddlers is often the regular and prolonged use of a feeding-bottle. Their teeth are usually so severely carious that the only treatment possible is either to extract or to fit crowns. Crowns for the front teeth are available in several types. With white acrylic facing, stainless steel crowns are very resistant and aesthetically appealing choice. Even by deep carious cavitation’s on anterior teeth or when root canal treatment for the primary teeth is necessary, white stainless steel crowns are the best choice.
Another possibility available for anterior teeth caries are strip-crowns. These are tiny little plastic pre-formed caps that are used to form the crown. The strip-crowns are filled with composite and like a filling the remnant of the crown is restored.
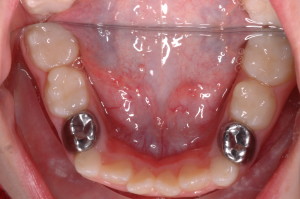
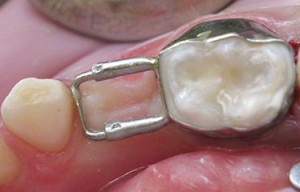
Space Maintainers
The primary molars have an important function of maintaining the space for the permanent teeth. If the baby’s tooth is lost prematurely, you may need a Space Maintainer to “fill” the space.
Baby teeth (dentists call them primary or deciduous teeth) aren’t just for chewing. Each one also acts as a guide for the permanent tooth that replaces it. If a primary tooth is lost too early, the permanent tooth loses its guide and can drift or erupt incorrectly into the mouth. Neighboring teeth also can move or tilt into the space, so the permanent tooth can’t come in.
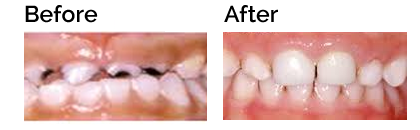
Breaking your child’s thumb sucking habit
Thumb sucking in young children is a very normal response to anxiety and stress. Many children are slow to break the habit which can lead to anxiety for parents. Is it worth the stress to break the thumb sucking habit? Yes, because long-term thumb sucking can cause problems with chewing, speech, and facial appearance.
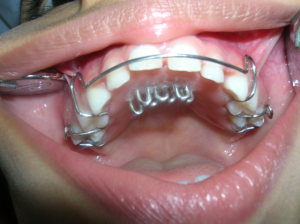
Effects on the jawbone
The longer and harder a child sucks his thumb the more harm is done to the teeth and jaws. Regular, strong thumb sucking makes front teeth move and can even reshape the jaw bone. Upper front teeth flare out and tip upward while lower front teeth move back and inward. Sucking on a thumb, finger, or blanket may be noted in preteens, teenagers and even adults. The initial orthodontic treatment is the same for all i.e., placement of a crib to break the habit.

